Hazardous Waste
Hazardous waste is any material that poses a threat to human health or the environment. This can include chemicals, heavy metals, medical waste, and other materials that are toxic, flammable, reactive, or corrosive. Proper management and disposal of hazardous waste are critical to prevent contamination of air, water, and soil.
Characteristics of Hazardous Waste
Hazardous waste can be identified by its characteristics:
- Ignitability: Waste that can easily catch fire.
- Corrosivity: Waste that can corrode metals or cause burns to human skin.
- Reactivity: Waste that is unstable and can create toxic gases, explosions, or other hazards.
- Toxicity: Waste that contains harmful substances at levels exceeding regulatory limits.
Types of Hazardous Waste
There are various types of hazardous waste, including:
- Industrial Waste: Generated by manufacturing processes and often contains chemicals and heavy metals.
- Household Hazardous Waste: Includes items like batteries, paints, and pesticides that should not be disposed of in regular trash.
- Medical Waste: Waste from healthcare facilities, such as sharps, expired medications, and infectious materials.
- E-Waste: Discarded electronic devices containing toxic materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium.
Management and Disposal
Proper management of hazardous waste involves:
- Identification: Classifying waste to determine its hazards and appropriate handling.
- Minimization: Reducing the amount of hazardous waste generated through waste reduction and recycling.
- Storage: Storing waste in secure containers and facilities to prevent leaks or spills.
- Transportation: Following regulations for transporting hazardous waste to treatment, storage, or disposal facilities.
- Disposal: Using methods such as incineration, landfilling, or chemical treatment in authorized facilities.
Regulations
Hazardous waste management is regulated by government agencies to ensure public and environmental safety. In the United States, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establish guidelines for handling and disposal of hazardous waste.
Study Guide
To study hazardous waste, focus on the following key points:
- Define hazardous waste and its characteristics.
- Identify examples of hazardous waste in different categories.
- Explain the management and disposal of hazardous waste.
- Understand the regulations and agencies involved in hazardous waste management.
- Discuss the environmental and health impacts of improper hazardous waste disposal.
Additionally, review case studies of hazardous waste incidents and explore current trends in hazardous waste management and technologies for treatment and disposal.
For further understanding, consider researching specific hazardous substances and their effects on human health and the environment.
By mastering these concepts, you will have a comprehensive understanding of hazardous waste and its significance in environmental sustainability and public health.
.◂Biology Worksheets and Study Guides High School. Cell processes
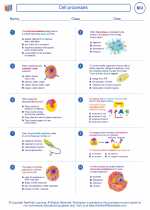
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key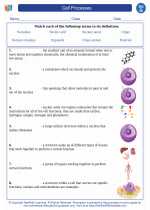
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key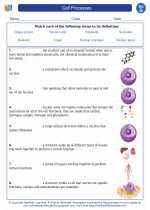
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
