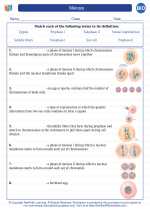
Topic: Snowy
Introduction to Snowy
Snow is a type of precipitation in the form of crystalline water ice, consisting of a multitude of snowflakes that fall from clouds. Snowy landscapes and weather conditions are of particular interest in various fields, including environmental science, geography, and meteorology. In this study guide, we will explore the scientific aspects of snowy environments, including their formation, ecological impact, and human interactions.
Formation of Snow
Snow forms when water vapor in the atmosphere undergoes deposition directly into ice crystals, bypassing the liquid phase. This process is influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of atmospheric particles known as ice nuclei. Understanding the formation of snow is crucial for predicting and managing snowy conditions.
Ecological Impact of Snowy Environments
Snowy environments play a vital role in various ecosystems, influencing factors such as water availability, temperature regulation, and habitat suitability for diverse organisms. Additionally, the reflective properties of snow impact climate patterns and contribute to regional and global climate dynamics. Studying the ecological impact of snowy environments provides insights into the interconnectedness of Earth's systems.
Human Interactions with Snowy Environments
Human societies have developed unique adaptations and technologies to thrive in snowy environments. From winter sports and recreation to transportation and infrastructure management, the interactions between humans and snowy landscapes are multifaceted. Understanding these interactions is essential for sustainable development and resource management in regions affected by snowfall.
Study Guide Questions
- What are the key factors influencing the formation of snow?
- Discuss the ecological significance of snowy environments in relation to global climate patterns.
- How do human societies adapt to and interact with snowy landscapes?
Exploring the topic of "snowy" encompasses a wide range of scientific, environmental, and social considerations. By delving into the formation, ecological impact, and human interactions with snowy environments, we gain a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics at play in these unique landscapes.
.◂Biology Worksheets and Study Guides High School. Meiosis

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key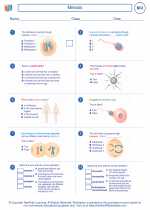
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key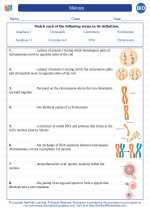
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key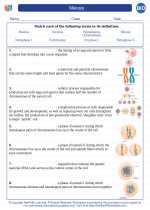
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key