Wetlands
Wetlands are areas where the land is saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally. They are characterized by the presence of water-tolerant vegetation and unique soil types. Wetlands play crucial ecological roles, serving as habitats for diverse plant and animal species, regulating water flow, and providing numerous ecosystem services.
Types of Wetlands
There are several different types of wetlands, including:
- Marshes: Wetlands dominated by herbaceous plants and grasses
- Swamps: Wetlands dominated by trees and shrubs
- Bogs: Acidic wetlands characterized by peat deposits and specialized plant species
- Fens: Wetlands fed by groundwater and characterized by alkaline water and peat deposits
Ecological Importance
Wetlands provide a wide range of ecological benefits, including:
- Biodiversity: Wetlands support a rich diversity of plant and animal species, many of which are specially adapted to wetland environments.
- Water Filtration: Wetlands act as natural filters, trapping sediments and pollutants from water, thus improving water quality.
- Flood Control: Wetlands help to absorb and store excess water during periods of heavy rain, reducing the risk of flooding in adjacent areas.
- Carbon Sequestration: Peatlands, a type of wetland, store large amounts of carbon, helping to mitigate climate change.
Threats to Wetlands
Despite their ecological importance, wetlands are under threat from various human activities, including urban development, agricultural expansion, and pollution. These activities can lead to the loss and degradation of wetland habitats, impacting the species that depend on them and reducing the benefits they provide to society.
Study Guide
To effectively study the topic of wetlands, consider the following key points:
- Understand the defining characteristics of wetlands, including soil types, hydrology, and vegetation.
- Explore the different types of wetlands and the specific characteristics of each type.
- Learn about the ecological functions and services provided by wetlands, such as biodiversity support, water filtration, and flood control.
- Investigate the threats facing wetlands and the potential consequences of wetland loss and degradation.
- Consider the conservation and management strategies aimed at protecting and restoring wetland ecosystems.
By mastering these key points, you will develop a comprehensive understanding of wetlands and their significance in the natural world.
.◂Biology Worksheets and Study Guides High School. Meiosis

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key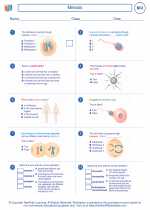
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key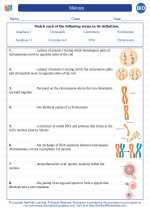
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key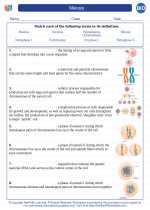
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key