Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. When an object accelerates, it is either speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction.
Formulas for Acceleration
The formula for acceleration is:
center;">a = (vf - vi) / t
where:
Units of Acceleration
The SI unit for acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s2).
Types of Acceleration
There are three main types of acceleration:
- Positive Acceleration: When an object is speeding up, its acceleration is positive.
- Negative Acceleration (Deceleration): When an object is slowing down, its acceleration is negative.
- Uniform Acceleration: When an object's velocity changes by the same amount in each equal time period, it is said to be undergoing uniform acceleration.
Examples of Acceleration
Some common examples of acceleration include:
Study Guide for Acceleration
To understand acceleration, it is important to grasp the following concepts:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Earth's resources
Study Guide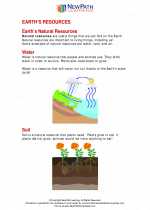 Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE (NGSS)
Earth’s Place in the Universe
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Use observations of the sun, moon, and stars to describe patterns that can be predicted.
Make observations at different times of year to relate the amount of daylight to the time of year.