Carbonate Minerals
Carbonate minerals are a diverse group of minerals containing the carbonate ion, CO3^2-. They are formed through the combination of carbon, oxygen, and a metal ion, such as calcium, magnesium, or iron. These minerals are an essential part of the Earth's crust and play a vital role in various geological processes. Some common carbonate minerals include calcite, aragonite, and dolomite.
Properties of Carbonate Minerals
- Chemical Composition: Carbonate minerals are composed of the carbonate ion combined with a metal ion.
- Hardness: Most carbonate minerals have a relatively low to medium hardness. For example, calcite has a hardness of 3 on the Mohs scale.
- Crystal Structure: Carbonate minerals often form rhombohedral crystals, but they can also occur in massive, granular, or fibrous forms.
- Reaction with Acid: Many carbonate minerals effervesce (fizz) when they come into contact with weak acids due to the release of carbon dioxide gas.
Formation and Occurrence
Carbonate minerals are commonly formed in marine and freshwater environments through the precipitation of dissolved carbonates. They can also be found in sedimentary rocks, hydrothermal veins, and metamorphic rocks. Fossilized carbonate minerals are important indicators of past environmental conditions and can provide valuable information about Earth's history.
Uses and Economic Importance
Carbonate minerals have a wide range of practical applications. For example, calcite is used in the production of lime and cement, as a soil conditioner, and in the manufacturing of optical instruments. Dolomite is used as a source of magnesium and as a decorative stone. Additionally, carbonate minerals are essential components of many building materials and industrial products.
Study Guide
- What is the chemical composition of carbonate minerals?
- Describe the crystal structure of carbonate minerals.
- Explain how carbonate minerals are formed and where they are commonly found.
- Discuss the practical uses and economic importance of carbonate minerals.
- Identify at least three common carbonate minerals and their distinct properties.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Earth's resources
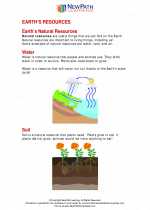
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
