Cosmology Study Guide
1. Big Bang Theory
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the observable universe. It states that the universe originated from a single, extremely dense and hot point, and has been expanding and cooling ever since.
2. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation is the afterglow of the Big Bang. It is a faint glow of light that fills the universe and provides crucial evidence for the Big Bang theory.
3. Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Dark matter and dark energy are two mysterious components that make up the majority of the universe's mass-energy content. Dark matter is invisible and detectable only through its gravitational effects, while dark energy is thought to be responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe.
4. Formation and Evolution of Galaxies
Cosmology studies the formation and evolution of galaxies, including how they are distributed in the universe and how they have changed over cosmic time.
5. Cosmological Models
Cosmologists develop mathematical models to describe the universe's behavior and predict its future. These models often include concepts such as inflation, cosmic inflation, and the multiverse.
6. Observational Cosmology
Observational cosmology involves using telescopes and other instruments to study the universe and gather data that can be used to test cosmological theories and models.
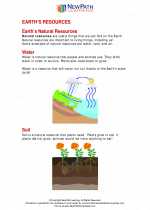
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Earth's resources
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
