Neutrons
Neutrons are subatomic particles that are found within the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass similar to protons but carry no electrical charge, making them electrically neutral. Neutrons play a crucial role in determining the stability and behavior of an atom.
Structure of Neutrons
Neutrons are composed of three quarks - two down quarks and one up quark. The interaction between these quarks and the strong nuclear force is what holds the neutron together.
Role of Neutrons
Neutrons contribute to the stability of the atomic nucleus. They help bind protons together through the strong nuclear force, preventing the repulsion between positively charged protons. Neutrons also play a key role in nuclear reactions and nuclear fission processes.
Study Guide
- What is the mass and charge of a neutron?
- Describe the structure of a neutron.
- Explain the role of neutrons in determining the stability of an atom.
- How do neutrons contribute to nuclear reactions?
- What is the strong nuclear force, and how does it relate to the stability of neutrons?
[Neutrons] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Earth's resources
Study Guide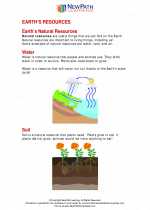 Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earth's resources
Earth's resources 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE (NGSS)
Earth’s Place in the Universe
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Use observations of the sun, moon, and stars to describe patterns that can be predicted.
Make observations at different times of year to relate the amount of daylight to the time of year.