Infectious Agents
Infectious agents are microorganisms that can cause disease in living organisms. There are several types of infectious agents, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites.
Types of Infectious Agents
- Viruses: These are tiny infectious agents that can only replicate inside the cells of an organism. Common examples include the influenza virus and the common cold virus.
- Bacteria: These are single-celled microorganisms that can cause a range of illnesses, from strep throat to tuberculosis.
- Fungi: Fungi can cause infections such as athlete's foot and ringworm. They can also cause more serious systemic infections in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Parasites: Parasites are organisms that live on or inside another organism and benefit at the host’s expense. Examples include malaria-causing Plasmodium parasites and intestinal worms.
How Infectious Agents Spread
Infectious agents can spread in various ways, including:
- Direct Contact: This can occur through physical contact with an infected person, such as touching, kissing, or sexual intercourse.
- Indirect Contact: Infectious agents can spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects, such as doorknobs, utensils, or shared toys.
- Respiratory Droplets: When an infected person coughs or sneezes, respiratory droplets containing infectious agents can be inhaled by others.
- Vector-Borne Transmission: Some infectious agents are spread through the bites of insects or other arthropods, such as mosquitoes carrying the malaria parasite.
Preventing the Spread of Infectious Agents
There are several measures that can help prevent the spread of infectious agents:
- Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing with soap and water can help prevent the spread of infectious agents.
- Immunization: Vaccines can protect against certain infectious agents, helping to prevent their spread.
- Safe Food and Water: Proper food handling and clean drinking water can reduce the risk of ingesting infectious agents.
- Quarantine and Isolation: Keeping infected individuals away from others can help prevent the spread of infectious agents.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about infectious agents:
- What are the main types of infectious agents?
- How do infectious agents spread?
- What are some measures to prevent the spread of infectious agents?
Be sure to review the types of infectious agents and their characteristics, as well as the various modes of transmission and prevention strategies.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Human body
Study Guide Human body
Human body  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson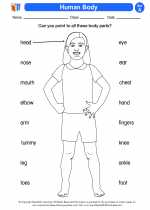 Human Body
Human Body  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Human body
Human body  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Human body
Human body  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Human body
Human body  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key My Senses
My Senses  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Human Body
Human Body  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key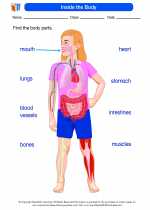 Inside the Body
Inside the Body  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key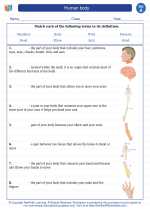 Human body
Human body  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Human body
Human body 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Design a solution to a human problem by using materials to imitate how plants and/or animals use their external parts to help them survive, grow, and meet their needs (e.g., outerwear imitating animal furs for insulation, gear mimicking tree bark or shells for protection).