Light Energy
Light energy is a form of energy that is visible to the human eye. It is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is made up of tiny particles called photons. Light energy is essential for life on Earth and plays a crucial role in many natural processes.
Properties of Light Energy
Light energy travels in straight lines and can pass through some objects, such as glass and water. It can be reflected, refracted, and absorbed by different materials. Light energy can also be separated into its different colors through a process called dispersion.
Sources of Light Energy
The primary source of light energy is the sun, which emits light through a process called nuclear fusion. Other sources of light energy include artificial light sources such as light bulbs, candles, and fire.
Uses of Light Energy
Light energy has numerous practical applications, including providing illumination for visibility, enabling photosynthesis in plants, and allowing for the creation of images in photography and cinematography. It is also used in various technologies such as lasers, fiber optics, and solar panels.
How We See Light
When light energy enters the eye, it passes through the cornea and lens before reaching the retina. The retina contains cells called photoreceptors, which convert light energy into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The brain then processes these signals to create the sensation of sight.
Study Guide
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Human body

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson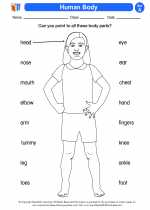
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key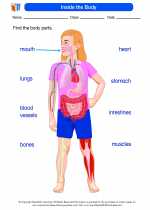
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key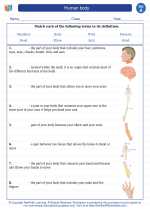
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
