Viruses
Viruses are microscopic infectious agents that can only replicate inside the cells of a living organism. They are made up of genetic material, either DNA or RNA, surrounded by a protein coat.
Here are some key points to study about viruses:
- Structure: Viruses are composed of genetic material, either DNA or RNA, surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid.
- Reproduction: Viruses cannot reproduce on their own and must infect a host cell to replicate. Once inside a host cell, they take over the cell's machinery to produce more viruses.
- Classification: Viruses are classified based on their genetic material, shape, and replication method. They can infect animals, plants, and even bacteria.
- Effects: Viruses can cause a wide range of effects on their host, from mild illnesses like the common cold to more severe diseases like HIV, Ebola, and COVID-19.
- Prevention and Treatment: Vaccines are used to prevent viral infections, and antiviral medications can help treat some viral illnesses. However, many viruses do not have a specific treatment.
Understanding viruses is important in the fields of medicine, biology, and public health, as they play a significant role in infectious diseases and have a major impact on human and animal health.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. My senses
Study Guide My senses
My senses  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson My Senses
My Senses  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key My senses
My senses  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key My senses
My senses  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key My senses
My senses  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key My senses
My senses  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key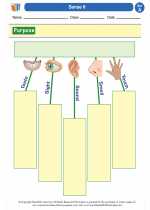 Sense It
Sense It  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key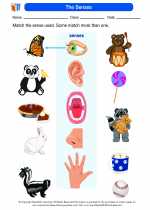 The Senses
The Senses  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key My senses
My senses 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE (NGSS)
Waves and their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Make observations to construct an evidence-based account that objects can be seen only when illuminated.