Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a structure found in the cells of plants and animals. It is a stack of membrane-bound sacs that are responsible for processing, packaging, and distributing molecules within or outside of the cell.Structure of the Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is made up of flattened sacs called cisternae. These cisternae are stacked on top of each other, and each stack is surrounded by vesicles. The Golgi apparatus is typically located near the nucleus of the cell.Functions of the Golgi Apparatus
1. Processing: The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids that are made by the endoplasmic reticulum. It adds carbohydrate chains to proteins to form glycoproteins.2. Packaging: Once the molecules have been processed, the Golgi apparatus packages them into vesicles for transport to different parts of the cell or for release from the cell.3. Distribution: The Golgi apparatus sends the packaged molecules to their correct destinations within the cell or releases them outside the cell through the process of exocytosis.Importance of the Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is crucial for the proper functioning of the cell. It ensures that proteins and lipids are processed correctly and sent to the right places within the cell or outside of it.Study Guide
Now that you've learned about the Golgi apparatus, here are a few questions to test your understanding:.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Second Grade. Comparing matter
Study Guide Comparing matter
Comparing matter  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson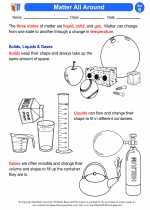 Matter All Around
Matter All Around  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Comparing matter
Comparing matter  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Comparing matter
Comparing matter  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Comparing matter
Comparing matter  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Comparing matter
Comparing matter 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE (NGSS)
Matter and its Interactions
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Construct an argument with evidence that some changes caused by heating or cooling can be reversed and some cannot.