Limbic System
The limbic system is a complex set of structures in the brain that is involved in the regulation of emotions, memory, and arousal. It is located between the brainstem and the two cerebral hemispheres. The limbic system plays a key role in processing and regulating emotions, as well as forming and retrieving memories.
Structures of the Limbic System
The main structures of the limbic system include:
- Hippocampus: involved in the formation and retrieval of memories
- Amygdala: responsible for processing emotions, particularly fear and aggression
- Hypothalamus: regulates basic bodily functions such as hunger, thirst, and body temperature, and is involved in the release of certain hormones
- Thalamus: acts as a relay station for sensory information
- Cingulate gyrus: plays a role in emotional and cognitive processing
Functions of the Limbic System
The limbic system is involved in several important functions:
- Emotion processing: The amygdala and other limbic structures are involved in the processing and regulation of emotions.
- Memory formation and retrieval: The hippocampus is critical for the formation of new memories and the retrieval of old ones.
- Regulation of basic bodily functions: The hypothalamus helps regulate basic bodily functions such as hunger, thirst, and body temperature.
- Behavioral and motivational responses: The limbic system plays a role in generating behavioral and motivational responses to environmental stimuli.
Study Guide
To study the limbic system, consider the following key points:
- Identify the main structures of the limbic system and their functions.
- Understand the role of the limbic system in emotion processing and memory formation.
- Explore the interconnections between the limbic system and other brain regions.
- Investigate the impact of damage or dysfunction in the limbic system on emotional and cognitive functioning.
By understanding the limbic system and its functions, you can gain insight into the complex mechanisms underlying emotions, memory, and behavior.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Second Grade. Comparing matter
Study Guide Comparing matter
Comparing matter  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson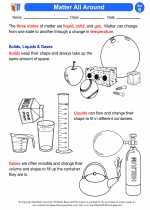 Matter All Around
Matter All Around  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Comparing matter
Comparing matter  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Comparing matter
Comparing matter  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Comparing matter
Comparing matter  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Comparing matter
Comparing matter 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE (NGSS)
Matter and its Interactions
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Construct an argument with evidence that some changes caused by heating or cooling can be reversed and some cannot.