Orbit
An orbit is the path that an object takes as it revolves around another object in space. Orbits are governed by the gravitational pull between the two objects. This means that the object in orbit is constantly falling towards the object it is orbiting, but its forward motion prevents it from actually colliding with the object. This balance between the forward motion and the gravitational pull keeps the object in a stable, repeating path around the other object.
Types of Orbits:
- Circular Orbit: When an object revolves around another object in a perfect circle, it is said to be in a circular orbit. The force of gravity is uniform in all directions in a circular orbit.
- Elliptical Orbit: In an elliptical orbit, the path of the orbiting object is an ellipse, not a perfect circle. This means that the distance between the two objects varies as the orbit progresses.
- Polar Orbit: A polar orbit is one in which the orbiting object passes above or nearly above both poles of the object being orbited on each revolution.
Factors Affecting Orbits:
Several factors can affect the path of an orbiting object:
- Gravitational Pull: The strength of the gravitational pull between the two objects determines the shape and size of the orbit.
- Velocity: The speed of the orbiting object affects the shape and size of the orbit. A faster object may have a larger orbit, while a slower object may have a smaller orbit.
- Mass of Objects: The mass of the objects involved also affects the orbit. A more massive object will have a greater influence on the orbiting object.
Applications of Orbits:
Understanding orbits is crucial for various applications in space exploration and satellite technology. For example, satellites are placed in specific orbits to ensure proper communication, weather monitoring, and navigation. Additionally, the study of orbits is fundamental in the field of astronomy for understanding the motion of celestial bodies.
Study Guide:
To understand orbits, it's important to grasp the concepts of gravity, motion, and the properties of objects in space. Here are some key points to focus on while studying orbits:
- Definition of orbit and its significance in space.
- Different types of orbits and their characteristics.
- Factors affecting orbits, such as gravitational pull, velocity, and mass of objects.
- Real-life applications of orbits in space exploration and satellite technology.
Additionally, it's helpful to explore examples of orbits in the solar system, such as the orbits of planets around the sun and the moon around Earth. Observing these natural orbits can provide valuable insights into the principles of orbital motion.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Third Grade. Changes on earth
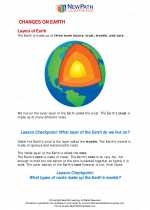
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
