Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the energy that an object has because of its motion and is directly proportional to its mass and the square of its velocity.
Formula for Kinetic Energy
The formula for kinetic energy is:
KE = 0.5 * mass * velocity2
Units of Kinetic Energy
The standard unit of kinetic energy is the joule (J). 1 joule is equal to 1 kilogram meter squared per second squared (kg·m2/s2).
Factors Affecting Kinetic Energy
The kinetic energy of an object depends on two factors:
- Mass: The greater the mass of an object, the greater its kinetic energy, assuming the velocity remains constant.
- Velocity: The kinetic energy of an object increases significantly with the increase in velocity. Since the kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the velocity, doubling the velocity will quadruple the kinetic energy.
Examples of Kinetic Energy
Examples of kinetic energy in everyday life include:
- A moving car
- A swinging pendulum
- A flying bird
- A rolling ball
Study Guide
To understand kinetic energy, it's important to remember the following key points:
- Understand the definition of kinetic energy and its formula.
- Learn how to calculate kinetic energy using the formula KE = 0.5 * mass * velocity2.
- Understand the relationship between mass, velocity, and kinetic energy.
- Practice solving problems involving kinetic energy using different mass and velocity values.
- Identify examples of kinetic energy in everyday life and observe how mass and velocity affect the kinetic energy of objects.
By mastering these concepts, you will have a solid understanding of kinetic energy and its role in the physical world.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Third Grade. Grouping of Animals
Study Guide Grouping of Animals
Grouping of Animals  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson Grouping of Animals
Grouping of Animals  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Grouping of Animals
Grouping of Animals  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Grouping of Animals
Grouping of Animals  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Grouping of Animals
Grouping of Animals  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Grouping of Animals
Grouping of Animals  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key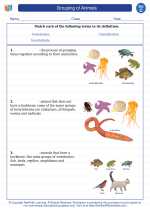 Grouping of Animals
Grouping of Animals 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Create representations to explain the unique and diverse life cycles of organisms other than humans (e.g., flowering plants, frogs, butterflies), including commonalities such as birth, growth, reproduction, and death.