Food webs/food chains -> adaptations
Structural Adaptations
Structural adaptations are physical features of an organism's body that help it survive in its environment. Examples of structural adaptations include the shape of a bird's beak, the coloration of an animal's fur, or the size and shape of a plant's leaves. These features are often specialized to perform specific functions that aid in survival, such as obtaining food or avoiding predators.
Behavioral Adaptations
Behavioral adaptations are actions or patterns of behavior that help an organism survive. These adaptations may include migration, hibernation, courtship rituals, or the way an animal builds its nest. Behavioral adaptations are learned or instinctual behaviors that improve an organism's chances of survival and reproduction.
Functional Adaptations
Functional adaptations are internal physiological or biochemical changes that help an organism survive. These adaptations may include the ability to detoxify harmful substances, the capacity to withstand extreme temperatures, or the efficiency of an animal's respiratory system. Functional adaptations often involve the workings of an organism's internal systems to cope with environmental challenges.
Examples of Adaptations
Some examples of adaptations in living organisms include:
- The long neck of a giraffe, which helps it reach leaves high in trees for food
- The camouflage of a chameleon, which allows it to blend in with its environment and avoid predators
- The migration of birds, which enables them to find food and suitable nesting sites in different seasons
- The thick fur of Arctic animals, which provides insulation against cold temperatures
Study Guide
To understand adaptations, it's important to consider the following questions:
- What are the different types of adaptations?
- How do structural adaptations differ from behavioral and functional adaptations?
- What are some examples of structural, behavioral, and functional adaptations in plants and animals?
- How do adaptations help organisms survive in their environments?
- What role does natural selection play in the development of adaptations?
By exploring these questions and examples, you can gain a deeper understanding of how living organisms have evolved to thrive in diverse environments through their adaptations.
[Adaptations] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson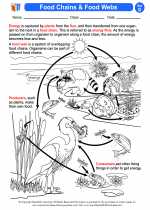
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
