Applications of Bioelectricity
Bioelectricity refers to the electrical potentials and currents that are produced by or occur within living organisms. The study of bioelectricity has led to various applications across different fields including medicine, neuroscience, and technology. Here are some of the key applications of bioelectricity:
Medical Devices
Bioelectricity is used in a wide range of medical devices such as pacemakers, defibrillators, and electroencephalography (EEG) machines. These devices utilize bioelectric signals to monitor and regulate the electrical activity of the heart, brain, and other vital organs.
Neuroscience Research
Researchers use bioelectric signals to study the functions of the nervous system. Techniques such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and nerve conduction studies help neuroscientists understand brain activity, diagnose neurological disorders, and develop treatments for conditions such as epilepsy and Parkinson's disease.
Biotechnology
Bioelectricity plays a crucial role in biotechnology, particularly in the field of bioinstrumentation. Biosensors, for example, detect and measure biological and chemical substances by converting bioelectric signals into measurable outputs. Additionally, bioelectricity is used in techniques like electroporation, which introduces DNA and other molecules into cells for genetic manipulation and gene therapy.
Regenerative Medicine
Electric fields have been shown to influence the growth and regeneration of tissues. Researchers are exploring the use of bioelectricity to promote wound healing, tissue regeneration, and the development of bioelectric scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.
Study Guide
To better understand the applications of bioelectricity, consider the following study guide:
- Describe the role of bioelectricity in medical devices and provide examples of such devices.
- Explain how bioelectric signals are utilized in neuroscience research and diagnosis of neurological disorders.
- Discuss the applications of bioelectricity in biotechnology, with a focus on biosensors and electroporation.
- Explore the potential of bioelectricity in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
- Research and present a case study or recent development in the field of bioelectricity and its applications.
By exploring these topics, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the diverse applications of bioelectricity and its significance in various scientific and medical fields.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson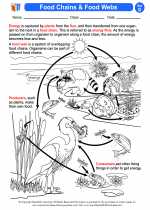
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
