Food webs/food chains -> carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide: An Overview
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom. It is a colorless and odorless gas that is naturally present in the Earth's atmosphere.
Properties of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a non-flammable gas that is denser than air. It is soluble in water, and when dissolved, it forms a weakly acidic solution due to the formation of carbonic acid. At standard temperature and pressure, carbon dioxide exists as a gas, but it can be converted to a solid form (dry ice) at temperatures below -78.5 degrees Celsius.
Sources and Production
Carbon dioxide is produced through various natural and human activities. Natural sources include volcanic eruptions, respiration in living organisms, and the decay of organic matter. Human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, industrial processes, and deforestation also contribute to the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Role in the Environment
Carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in the Earth's carbon cycle. It is a greenhouse gas, meaning it can trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect. This natural phenomenon helps regulate the Earth's temperature, making it suitable for supporting life. However, an excess of carbon dioxide due to human activities has led to an increase in the greenhouse effect, resulting in global climate change and ocean acidification.
Study Guide: Understanding Carbon Dioxide
- Define carbon dioxide and its chemical composition.
- Describe the physical properties of carbon dioxide.
- Identify natural and human sources of carbon dioxide.
- Explain the role of carbon dioxide in the Earth's carbon cycle.
- Discuss the environmental impact of excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
By understanding the properties and environmental impact of carbon dioxide, we can make informed decisions to mitigate its effects and work towards a more sustainable future.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson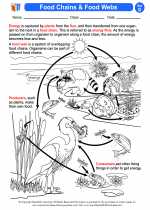
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
