Dendrites
Dendrites are the branch-like structures that extend from the cell body of a neuron. They act as the receiving end of the neuron, gathering information from other neurons and transmitting it to the cell body.
Structure of Dendrites
Dendrites are covered in tiny projections called dendritic spines, which increase the surface area available for receiving signals from other neurons. These spines play a crucial role in synaptic transmission and plasticity.
Function of Dendrites
The main function of dendrites is to receive signals from other neurons and transmit these signals to the cell body. The dendrites integrate these signals and, if the combined input is strong enough, they generate an electrical signal that travels down the axon to communicate with other neurons.
Study Guide
- What are dendrites and what is their function?
- Describe the structure of dendrites and the role of dendritic spines.
- Explain the process of signal transmission in dendrites.
- Discuss the importance of dendrites in neural communication.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains
Study Guide Food webs/food chains
Food webs/food chains  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson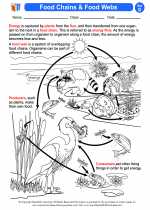 Food Chains & Food Webs
Food Chains & Food Webs  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Food webs/food chains
Food webs/food chains  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Food webs/food chains
Food webs/food chains  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Food webs/food chains
Food webs/food chains  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Food Chains & Food Webs
Food Chains & Food Webs  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Food webs/food chains
Food webs/food chains  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Food webs/food chains
Food webs/food chains  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Food webs/food chains
Food webs/food chains 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Concepts of Life Science (SC1, SC2, SC3)
The student demonstrates an understanding that all organisms are linked to each other and their physical environments through the transfer and transformation of matter and energy by identifying examples of living and non-living things and the relationship between them (e.g., living things need water, herbivores need plants).
The student demonstrates an understanding that all organisms are linked to each other and their physical environments through the transfer and transformation of matter and energy by identifying a simple food chain of familiar plans and animals, diagramming how energy flows through it, and describing the effects of removing one link.
Concepts of Life Science: A student should understand and be able to apply the concepts, models, theories, facts, evidence, systems, and processes of life science. A student who meets the content standard should:
Develop an understanding that all organisms are linked to each other and their physical environments through the transfer and transformation of matter and energy.