Food webs/food chains -> human body
Human Body
Welcome to the study guide for the human body! The human body is a complex and fascinating system made up of various organs and tissues that work together to keep us alive and functioning. In this guide, we will explore the different systems of the human body and how they work together to maintain homeostasis.
The Skeletal System
The skeletal system is the framework of the body, consisting of bones and connective tissues. Its main functions include providing support, protection, and movement for the body. There are 206 bones in the adult human body, and they come in different shapes and sizes. The bones also produce red and white blood cells and store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus.
The Muscular System
The muscular system is responsible for movement and locomotion. There are three types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and work in pairs to move the body. Smooth muscles are found in the walls of internal organs and blood vessels, while cardiac muscles are found in the heart.
The Circulatory System
The circulatory system, also known as the cardiovascular system, is responsible for transporting blood, oxygen, and nutrients throughout the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through the blood vessels to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues and organs.
The Respiratory System
The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. It includes the nose, trachea, and lungs. When we inhale, the lungs take in oxygen, and when we exhale, they expel carbon dioxide. The respiratory system also helps regulate the body's pH balance.
The Digestive System
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and intestines. The digestive process begins in the mouth, where food is chewed and mixed with saliva. It then travels to the stomach and intestines, where nutrients are absorbed and waste is eliminated.
The Nervous System
The nervous system is the body's communication network, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It is responsible for receiving and sending signals throughout the body, allowing us to sense and respond to the environment. The nervous system also controls voluntary and involuntary actions.
The Endocrine System
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, which regulate various bodily functions. It includes the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and adrenal glands, among others. Hormones act as chemical messengers, controlling processes such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Study Guide Questions
- What are the main functions of the skeletal system?
- How do muscles work together to produce movement?
- Describe the pathway of blood through the circulatory system.
- What is the role of the respiratory system in maintaining homeostasis?
- What are the main organs of the digestive system, and what are their functions?
- Explain the functions of the nervous system in the human body.
- How do hormones regulate bodily functions in the endocrine system?
Use these questions to review and test your understanding of the human body. Understanding how these systems work together is crucial to understanding the complexities of the human body and how it functions.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson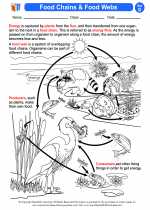
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
