Food webs/food chains -> nuclear energy
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is the energy that is released during nuclear reactions. This energy can be harnessed and used to generate electricity. The two main nuclear reactions that release nuclear energy are nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is the process of splitting the nucleus of an atom into two smaller nuclei. This process releases a large amount of energy in the form of heat. The most commonly used fuel for nuclear fission is uranium-235. When a uranium-235 nucleus is bombarded with neutrons, it becomes unstable and splits into two smaller nuclei, releasing additional neutrons and a large amount of energy. These released neutrons can then go on to initiate more fission reactions, creating a self-sustaining chain reaction.
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process of combining the nuclei of two atoms to form a heavier nucleus. This process also releases a significant amount of energy. The sun and other stars produce energy through nuclear fusion reactions, which involve the fusing of hydrogen nuclei to form helium. While nuclear fusion has the potential to produce large amounts of energy, it is currently difficult to achieve and sustain on Earth due to the high temperatures and pressures required to initiate the reactions.
How Nuclear Energy is Used
When nuclear fission reactions occur in a controlled environment, such as a nuclear power plant, the heat generated from the reactions is used to produce steam. This steam then drives turbines connected to generators, producing electricity. Nuclear power plants are able to generate a large amount of electricity without producing greenhouse gases or other air pollutants commonly associated with fossil fuel-based power plants.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
One of the main advantages of nuclear energy is that it is a low-carbon energy source, meaning it does not contribute significantly to climate change. Additionally, nuclear power plants can produce a large amount of electricity using relatively small amounts of fuel. However, nuclear energy also presents challenges, including the safe handling and disposal of radioactive waste, the potential for nuclear accidents, and the risk of nuclear proliferation.
Study Guide: Nuclear Energy
- What is nuclear energy?
- Explain the process of nuclear fission.
- Describe the potential of nuclear fusion for energy production.
- How is nuclear energy used to generate electricity?
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy.
For further study, you can explore the history of nuclear energy, the design and operation of nuclear power plants, and the ongoing research into advanced nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors and nuclear fusion reactors.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson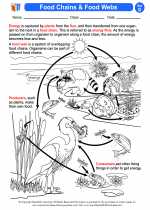
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
