Permanent Magnets
Permanent magnets are materials that produce a magnetic field. Unlike temporary magnets, such as electromagnets, permanent magnets do not rely on an external source of electrical power to maintain their magnetic properties. They are commonly used in everyday objects such as refrigerator magnets, speakers, and electric motors.
Magnetic Properties
Permanent magnets are characterized by their ability to attract ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt. They have two distinct poles - a north pole and a south pole. These poles create a magnetic field that exerts a force on other magnets and magnetic materials.
Types of Permanent Magnets
There are several types of permanent magnets, including:
- Alnico Magnets: Made from aluminum, nickel, and cobalt, these magnets are known for their strong magnetic properties.
- Ferrite Magnets: Also called ceramic magnets, these are made from iron oxide and other metallic elements. They are widely used in applications such as refrigerator magnets.
- Neodymium Magnets: These rare-earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets available. They are used in high-performance electronics and industrial applications.
How Permanent Magnets Work
At the atomic level, permanent magnets consist of tiny magnetic domains that align in a particular direction, creating a net magnetic field. This alignment is achieved during the manufacturing process and is responsible for the magnet's ability to retain its magnetic properties over time.
Uses of Permanent Magnets
Permanent magnets have a wide range of applications, including:
- Electric motors and generators
- Speakers and headphones
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines
- Magnetic compasses
- Security systems
Study Guide for Permanent Magnets
To understand permanent magnets, students should focus on the following key points:
- Identify the properties of permanent magnets, including their ability to attract ferromagnetic materials and their two distinct poles.
- Describe the different types of permanent magnets, such as alnico, ferrite, and neodymium magnets, and their respective uses.
- Explain the atomic-level behavior of permanent magnets and how magnetic domains contribute to their magnetic properties.
- Discuss real-world applications of permanent magnets in various devices and systems.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson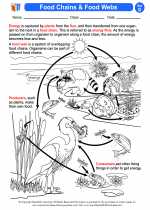
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
