Sun
The sun is a star at the center of our solar system. It is a nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, with internal convective motion that generates a magnetic field via a dynamo process. The sun is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. It provides the light and warmth necessary for the existence of life on our planet.
Structure of the Sun
The sun is composed of several layers, including the core, the radiative zone, the convective zone, the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The core is the innermost part where nuclear fusion occurs, generating the sun's energy. The photosphere is the visible surface of the sun, and the corona is the outermost layer of the sun's atmosphere.
Solar Energy
The sun's energy is produced by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, where hydrogen is converted into helium. This process releases a tremendous amount of energy in the form of light and heat, which is radiated out into space and reaches the Earth.
Effects of the Sun
The sun has a profound impact on Earth and its inhabitants. It drives the Earth's climate and weather patterns, influences the growth of plants through photosynthesis, and provides the energy that powers the water cycle. However, excessive exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation can also be harmful to living organisms, causing sunburn and increasing the risk of skin cancer.
Study Guide
- What is the sun?
- Describe the structure of the sun.
- How does the sun produce energy?
- What are the effects of the sun on Earth?
For further understanding of the sun, it is recommended to study the solar system, the electromagnetic spectrum, and the impacts of solar activity on Earth.
[Sun] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson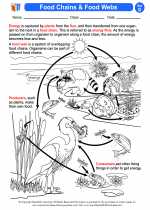
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
