Earthworms: A Fourth Grade Science Study Guide
Welcome to the study guide for earthworms! In this guide, we will explore the fascinating world of earthworms and learn about their characteristics, habitat, and importance in the ecosystem.
What are Earthworms?
Earthworms are small invertebrates that belong to the phylum Annelida. They are commonly found in soil and are known for their long, slender bodies and segmented appearance.
Anatomy of Earthworms
Earthworms have a tube-shaped body that is divided into segments. They have a head, which contains the mouth and sensory organs, and a tail. Earthworms also have a muscly organ called the clitellum, which is involved in reproduction.
Habitat of Earthworms
Earthworms are found in soil, where they burrow and create tunnels. They prefer moist, dark environments and are often found in gardens, forests, and agricultural fields.
Importance of Earthworms
Earthworms play a crucial role in the ecosystem. They help to improve soil structure by burrowing, which allows air and water to penetrate the soil. They also break down organic matter, such as dead leaves and plant material, into nutrients that can be used by plants.
Life Cycle of Earthworms
Earthworms are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive organs. However, they still need to mate with another earthworm to reproduce. After mating, the earthworms produce a cocoon from which young earthworms hatch.
Fun Facts about Earthworms
- Earthworms have no lungs, but instead breathe through their skin.
- Some species of earthworms can regenerate lost segments of their bodies.
- Earthworms can eat their own weight in organic matter every day.
Now that you have learned about earthworms, take some time to explore the world around you and see if you can find these fascinating creatures in action!
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Plant Structure and function

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key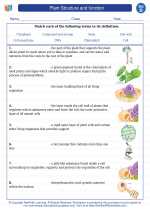
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key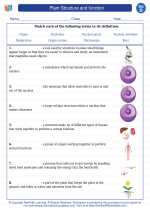
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
