Electricity
Electricity is a form of energy resulting from the existence of charged particles (such as electrons or protons), either statically as an accumulation of charge or dynamically as a current.
Key Concepts:
- Electric Charge: Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter. There are two types of charges: positive and negative. Like charges repel each other, and opposite charges attract each other.
- Electric Circuit: An electric circuit is a closed loop through which an electric current can flow. It consists of components such as a voltage source (e.g., battery), conductors (wires), and load (e.g., light bulb).
- Electric Current: Electric current is the flow of electric charge. It is measured in amperes (A) and is the rate of flow of electrons through a conductor.
- Voltage: Voltage is the electric potential difference between two points. It is measured in volts (V) and determines the force that drives the electric current through a circuit.
- Resistance: Resistance is a measure of how much a material or component opposes the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms (Ω).
- Conductors and Insulators: Conductors are materials that allow electric current to flow easily, while insulators are materials that resist the flow of electric current.
Study Guide:
- What is electric charge, and what are the two types of charges?
- Describe the components of an electric circuit and their functions.
- How is electric current measured, and what is its SI unit?
- Explain the concept of voltage and its role in an electric circuit.
- Define resistance and provide examples of materials with high and low resistance.
- Differentiate between conductors and insulators, and provide examples of each.
[Electricity] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Plant Structure and function
Study Guide Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key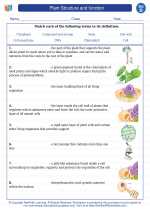 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key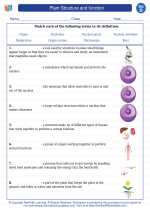 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE (NGSS)
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.