Electromagnets
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. When electric current flows through a wire, it creates a magnetic field around the wire. This magnetic field can be intensified by coiling the wire around a core material such as iron.
How does an electromagnet work?
When an electric current flows through a wire, it creates a magnetic field around the wire according to the right-hand rule. This magnetic field can be strengthened by coiling the wire around a core material, such as iron, to create an electromagnet. The strength of the magnetic field can be controlled by adjusting the amount of current flowing through the wire.
Applications of electromagnets
Electromagnets are used in a wide range of applications, including electric motors, generators, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, and magnetic separation processes.
Study Guide
- What is an electromagnet?
- How does an electric current create a magnetic field?
- What is the role of a core material in an electromagnet?
- Explain the applications of electromagnets in everyday life.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Plant Structure and function

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key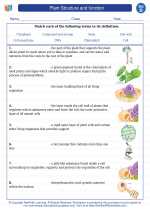
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key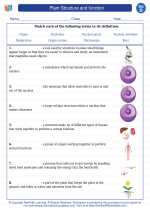
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
