Plant Structure and function -> flowers
Flowers
Flowers are the reproductive structures found in flowering plants (angiosperms). They are important for sexual reproduction in plants and come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and colors.
Structure of a Flower
A typical flower consists of several parts:
- Petal: Often colorful and scented, petals attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies.
- Sepal: These are the outermost part of the flower, protecting the developing bud.
- Stamen: The male reproductive part of the flower, consisting of the anther and filament.
- Pistil: The female reproductive part of the flower, consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary.
Functions of Flowers
Flowers serve several important functions in the life cycle of a plant:
- Reproduction: Flowers produce seeds through the process of pollination and fertilization.
- Pollination: Pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma, either by wind, water, or animals.
- Seed Production: After pollination, the ovary of the flower develops into a fruit containing seeds.
Types of Flowers
Flowers can be classified into different types based on various characteristics:
- Complete vs. Incomplete Flowers: Complete flowers have all four main parts (petals, sepals, stamen, and pistil), while incomplete flowers lack one or more of these parts.
- Perfect vs. Imperfect Flowers: Perfect flowers have both stamens and pistils, while imperfect flowers have only one of these reproductive parts.
- Inflorescence: Some plants bear flowers in clusters known as inflorescences, which can have various arrangements and patterns.
Role of Flowers in Human Life
Besides their biological significance, flowers have cultural, aesthetic, and economic importance in human society:
- Ornamental Purposes: Flowers are widely used for decorative and ornamental purposes, such as in gardens, floral arrangements, and ceremonies.
- Food Production: Many fruits and vegetables that humans consume are derived from the flowers of plants.
- Medicinal Uses: Some flowers have medicinal properties and are used in traditional and modern medicine.
By understanding the structure and functions of flowers, we gain a deeper appreciation for the vital role they play in both the plant kingdom and human society.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Plant Structure and function
Study Guide Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key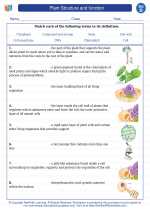 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key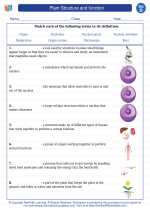 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE (NGSS)
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.