Plant Structure and function -> gene flow
Factors Affecting Gene Flow
Several factors can influence the rate of gene flow, including:
- Migration: The movement of individuals from one population to another is a key factor in gene flow. The more migration that occurs between populations, the greater the potential for gene flow.
- Barriers to Migration: Physical barriers such as mountains, rivers, or human-made structures can limit the movement of individuals between populations, reducing gene flow.
- Reproductive Compatibility: The ability of individuals from different populations to successfully interbreed can impact gene flow. If there are barriers to reproduction, gene flow may be limited.
Effects of Gene Flow
Gene flow can have several effects on populations and species:
- Increased Genetic Diversity: Gene flow can introduce new genetic variations into a population, increasing its overall genetic diversity.
- Homogenization of Populations: In some cases, gene flow can result in populations becoming more similar genetically, especially if there is extensive interbreeding between populations.
- Genetic Adaptation: The introduction of new genetic traits through gene flow can contribute to the adaptation of populations to their environments.
Study Guide
When studying gene flow, consider the following key points:
- Understand the concept of gene flow and its significance in population genetics.
- Explore the factors that can promote or limit gene flow between populations.
- Examine the effects of gene flow on genetic diversity, population homogenization, and genetic adaptation.
- Compare and contrast the impact of high versus low gene flow on the genetic makeup of populations.
- Consider real-life examples of gene flow in different species and ecosystems.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Plant Structure and function
Study Guide Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key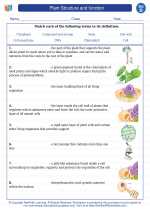 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key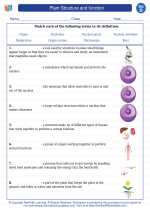 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE (NGSS)
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.