Plant Structure and function -> ground tissue
Ground Tissue
Ground tissue is one of the three main types of plant tissue, along with dermal tissue and vascular tissue. It is responsible for a variety of functions, including photosynthesis, storage, support, and secretion. Ground tissue is found in the roots, stems, and leaves of plants, and is made up of three main types of cells: parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
Types of Ground Tissue Cells
- Parenchyma cells: These are the most common type of plant cells and are involved in photosynthesis, storage of nutrients, and secretion. They have thin cell walls and are often found in the mesophyll of leaves.
- Collenchyma cells: These cells provide support to the plant and are often found in the petioles and young stems. They have unevenly thickened cell walls and can elongate as the plant grows.
- Sclerenchyma cells: These cells are specialized for support and protection. They have thick, lignified cell walls and are often found in the outer layers of stems and in seed coats.
Functions of Ground Tissue
Ground tissue performs several important functions in plants:
- Photosynthesis: Parenchyma cells in the leaves are responsible for carrying out photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
- Storage: Ground tissue stores various substances such as water, nutrients, and starch, which can be used by the plant as needed.
- Support: Collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells provide structural support to the plant, helping it to stand upright and resist mechanical stress.
- Secretion: Some types of ground tissue secrete substances that are important for plant defense, such as resins and gums.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about ground tissue:
- What are the three main types of ground tissue cells, and what are their respective functions?
- Where in the plant are parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells typically found?
- What are the main functions of ground tissue?
- How do parenchyma cells contribute to the process of photosynthesis?
- Why is the support provided by collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells important for the plant?
Understanding the role and structure of ground tissue is essential for comprehending the overall function of plants and their ability to thrive in various environments.
[Ground Tissue] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Plant Structure and function
Study Guide Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key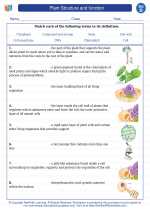 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key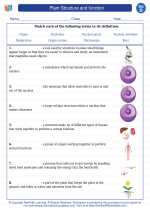 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE (NGSS)
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.