Plant Structure and function -> oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. By mass, oxygen is the third-most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium.
Properties of Oxygen:
- Physical State: Oxygen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas at room temperature and pressure.
- Chemical Reactivity: It is highly reactive and forms compounds with almost all other elements, as well as with many organic compounds.
- Role in Combustion: Oxygen supports combustion, and many materials ignite and burn more vigorously in its presence.
- Role in Respiration: Oxygen is essential for respiration in all aerobic organisms, as it is used during the process of cellular respiration to produce energy.
- Role in Ozone Layer: In the Earth's atmosphere, oxygen plays a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of the ozone layer, which protects life on Earth by filtering out harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Study Guide:
Here are some key points to remember about oxygen:
- What is the chemical symbol for oxygen?
- What is the physical state of oxygen at room temperature and pressure?
- What role does oxygen play in combustion?
- Why is oxygen essential for respiration in aerobic organisms?
- How does oxygen contribute to the formation and maintenance of the ozone layer in the Earth's atmosphere?
Understanding the properties and roles of oxygen is crucial in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
Feel free to explore further and conduct experiments to observe the properties and behavior of oxygen in different environments.
[Oxygen] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Plant Structure and function
Study Guide Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key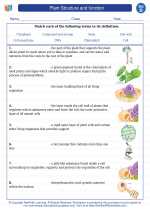 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key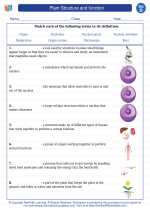 Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plant Structure and function
Plant Structure and function 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE (NGSS)
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.