Cytosol
The cytosol is the liquid component of the cytoplasm, the material within a cell that surrounds the organelles. It is a complex mixture of water, ions, small molecules, and large macromolecules such as proteins. Cytosol is involved in various cellular processes including metabolism, signaling, and transportation of molecules within the cell.
Composition of Cytosol
The cytosol is composed of:
- Water: The primary component of cytosol, making up the majority of its volume.
- Ions: Including potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Small Molecules: Such as sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids, which serve as energy sources and building blocks for cellular components.
- Macromolecules: Including proteins, RNA, and other biomolecules that play crucial roles in cellular function.
Functions of Cytosol
The cytosol serves several important functions within the cell:
- Metabolism: Many metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and protein synthesis, occur within the cytosol.
- Cellular Signaling: It is involved in signaling pathways that regulate various cellular processes, including growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
- Transport: Cytosol facilitates the movement of molecules and organelles within the cell through processes such as diffusion and cytoplasmic streaming.
- Storage: It serves as a reservoir for ions, nutrients, and other molecules required for cellular activities.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember when studying cytosol:
- Define cytosol and distinguish it from cytoplasm.
- Describe the composition of cytosol, including its major components.
- Explain the functions of cytosol in cellular metabolism, signaling, and transportation.
- Discuss the importance of cytosol in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Compare the roles of cytosol and other cellular compartments in supporting cellular function.
Understanding the role and composition of cytosol is fundamental to comprehending the complex processes that occur within a cell. It is important to grasp its significance in the context of cellular biology and its impact on overall cell function.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Electricity
Study Guide Electricity
Electricity  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson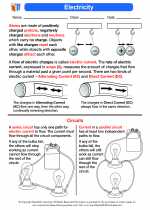 Electricity
Electricity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Electricity
Electricity 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Ask questions about data to determine the factors that affect the strength of electric and magnetic forces.