Nitrification
Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia or ammonium to nitrite followed by the oxidation of nitrite to nitrate by specialized bacteria. This process plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle, converting ammonia, which is toxic to many organisms, into nitrate, which can be taken up and used by plants.
Key Concepts
- Ammonia and Ammonium: These are forms of nitrogen that are produced from the decomposition of organic matter and the excretion of waste by organisms.
- Nitrite: This is an intermediate product formed during nitrification, which is further oxidized to form nitrate.
- Nitrate: This is the end product of nitrification, which can be used by plants as a source of nitrogen for growth.
- Nitrifying Bacteria: These are specialized bacteria that carry out the nitrification process in soil and water environments.
Process of Nitrification
Nitrification occurs in two main steps:
- Ammonia Oxidation: Ammonia or ammonium is oxidized to nitrite by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrosococcus species.
- Nitrite Oxidation: Nitrite is further oxidized to nitrate by nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) such as Nitrobacter and Nitrospira species.
Importance of Nitrification
Nitrification is important for several reasons:
- It converts toxic ammonia into less toxic forms of nitrogen.
- It provides a usable form of nitrogen (nitrate) for plants to support their growth and development.
- It contributes to the overall balance of nitrogen in ecosystems, helping to maintain the availability of nitrogen for living organisms.
Study Tips
When studying nitrification, consider the following tips:
- Understand the chemical reactions involved in the conversion of ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate.
- Learn about the specific bacteria involved in nitrification and their roles in the process.
- Explore the environmental factors that influence nitrification, such as pH, temperature, and oxygen availability.
- Consider the ecological implications of nitrification, including its effects on plant growth and nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Electricity
Study Guide Electricity
Electricity  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson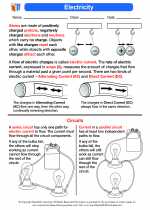 Electricity
Electricity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Electricity
Electricity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Electricity
Electricity 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Ask questions about data to determine the factors that affect the strength of electric and magnetic forces.