Spacecraft: Exploring the Final Frontier
Welcome to the fascinating world of spacecraft! In this study guide, we will explore the incredible machines that have allowed humans to journey beyond our planet and into the depths of outer space. From the early days of space exploration to the cutting-edge technology of today, spacecraft have played a pivotal role in expanding our understanding of the universe.
What is a Spacecraft?
A spacecraft is a vehicle designed for travel or operation in outer space. It can be manned or unmanned and is used for various purposes such as space exploration, satellite deployment, and scientific research.
Types of Spacecraft
There are several types of spacecraft, each designed for specific functions:
- Space Probes: Unmanned spacecraft designed to explore the solar system and beyond, gathering data and transmitting it back to Earth.
- Satellites: Spacecraft placed in orbit around a celestial body for communication, navigation, weather monitoring, and more.
- Space Shuttles: Reusable spacecraft used for carrying astronauts and cargo to and from space.
- Space Stations: Habitable spacecraft designed for long-term human presence in space, such as the International Space Station.
Parts of a Spacecraft
Spacecraft are made up of various components that enable them to function in the harsh environment of space:
- Propulsion System: Provides the necessary thrust for maneuvering and traveling through space.
- Payload: The instruments, equipment, or cargo carried by the spacecraft for its mission.
- Communication System: Allows the spacecraft to transmit data and receive instructions from mission control on Earth.
- Power Source: Provides energy to the spacecraft, often through solar panels or nuclear generators.
- Life Support System (for manned spacecraft): Provides astronauts with the necessary resources for survival in space, including air, water, and food.
Spacecraft Propulsion
There are different methods of propulsion used by spacecraft:
- Chemical Propulsion: Most commonly used for launching spacecraft into orbit and for making major trajectory changes.
- Electric Propulsion: Utilizes electric or magnetic fields to propel the spacecraft, offering greater fuel efficiency for long-duration missions.
- Nuclear Propulsion: Theoretical concept that involves using nuclear energy for propulsion, offering potentially faster travel speeds and shorter mission durations.
Challenges of Spacecraft
Spacecraft face numerous challenges in the hostile environment of space, including:
- Radiation: Exposure to high levels of cosmic and solar radiation can pose risks to both spacecraft and astronauts.
- Micrometeoroids: Tiny, high-speed particles in space can cause damage to spacecraft surfaces.
- Extreme Temperatures: Spacecraft must withstand both intense heat and bitter cold in the vacuum of space.
- Long Duration Missions: Manned spacecraft face the challenge of providing life support for astronauts on extended missions.
Future of Spacecraft
As technology continues to advance, the future of spacecraft holds exciting possibilities, including:
- Interplanetary Travel: Missions to Mars and beyond, paving the way for human exploration of other celestial bodies.
- Space Tourism: Commercial ventures offering private individuals the opportunity to travel to space.
- Advanced Propulsion Systems: Development of new propulsion technologies for faster and more efficient travel through space.
- Exploration of Exoplanets: Sending spacecraft to study planets orbiting distant stars.
With this study guide, you are now equipped to delve into the exciting world of spacecraft and the exploration of outer space. From the history of space exploration to the frontiers of future missions, the realm of spacecraft offers an endless source of wonder and discovery.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Electromagnetism

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson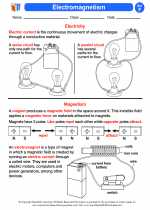
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
