Synthetic Rubber
Synthetic rubber is a man-made polymer material produced by the polymerization of various monomers. It is designed to mimic the properties of natural rubber, but with improved durability, resistance to heat, and other desirable characteristics. Synthetic rubber has a wide range of applications, including in the production of tires, industrial hoses, seals, and gaskets.
Types of Synthetic Rubber
There are several types of synthetic rubber, each with its own unique properties and uses:
- Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR): SBR is a widely used synthetic rubber with good abrasion resistance and aging stability. It is commonly used in tire manufacturing and as a substitute for natural rubber in various applications.
- Polybutadiene Rubber (BR): BR is known for its high resilience and low temperature flexibility, making it suitable for use in tire treads and conveyor belts.
- Neoprene Rubber: Neoprene is a versatile synthetic rubber with excellent resistance to oil, heat, and weathering. It is commonly used in gaskets, hoses, and wetsuits.
- Nitrile Rubber (NBR): NBR exhibits excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and chemicals, making it ideal for use in seals, gaskets, and O-rings in automotive and industrial applications.
- Butyl Rubber: Butyl rubber offers exceptional gas impermeability and weathering resistance, making it suitable for tire inner tubes, seals, and adhesives.
- EPDM Rubber: EPDM is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent weather resistance, ozone resistance, and electrical insulation properties. It is commonly used in roofing materials, automotive seals, and electrical insulation.
Production of Synthetic Rubber
The production of synthetic rubber involves the polymerization of monomers, which are small molecules that can react together to form long chains of polymers. The most common method of producing synthetic rubber is through the emulsion polymerization process, where monomers are suspended in water and polymerized to form latex. The latex can then be processed into various forms, such as sheets, pellets, or powders, depending on the intended application.
Study Guide
To understand synthetic rubber better, consider the following study guide questions:
- What are the main advantages of synthetic rubber over natural rubber?
- Describe the properties and applications of at least three types of synthetic rubber.
- Explain the polymerization process involved in the production of synthetic rubber.
- Compare and contrast the properties of natural rubber and synthetic rubber.
- Discuss the environmental impact of synthetic rubber production and potential sustainable alternatives.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Electromagnetism

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson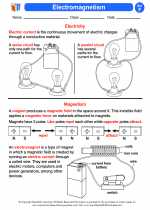
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
