Endocrine System
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that produce and release hormones to regulate many vital bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, sexual function, and mood. Unlike the nervous system, which uses electrical signals to transmit information, the endocrine system uses chemical messengers called hormones to communicate and coordinate various physiological processes.
Glands of the Endocrine System
The major glands of the endocrine system include:
- Hypothalamus: Located in the brain, it produces hormones that control the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
- Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the "master gland," it produces and secretes a variety of hormones that regulate other endocrine glands and various bodily functions.
- Thyroid Gland: Produces hormones that regulate metabolism and growth.
- Adrenal Glands: Produce hormones involved in stress response, metabolism, and blood pressure regulation.
- Pancreas: Produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels.
- Reproductive Glands: Including the ovaries and testes, which produce hormones involved in reproductive functions.
Hormones and Their Functions
Each gland in the endocrine system produces specific hormones, which have diverse effects on the body. Some important hormones and their functions include:
- Insulin: Regulates blood sugar levels by promoting the uptake of glucose by cells.
- Thyroid Hormones: Control metabolism and play a crucial role in growth and development.
- Adrenaline: Triggers the body's "fight or flight" response to stress.
- Estrogen and Testosterone: Regulate sexual development and reproductive functions.
- Growth Hormone: Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
Regulation of Hormone Release
Hormone release is tightly regulated through a complex feedback system. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland play key roles in monitoring hormone levels and coordinating the release of hormones from other glands. Additionally, negative feedback loops help maintain hormone balance by signaling the body to reduce hormone production when levels become too high.
Disorders of the Endocrine System
Imbalances in hormone levels can lead to various health problems. Common endocrine disorders include diabetes (caused by insufficient insulin production or inefficient use of insulin) and thyroid disorders (resulting from over- or underproduction of thyroid hormones).
Study Guide
To effectively study the endocrine system, consider the following key points:
- Understand the functions of major endocrine glands and the hormones they produce.
- Explore the role of hormones in regulating specific bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth, and stress response.
- Learn about the feedback mechanisms that regulate hormone release and maintain hormone balance.
- Review common endocrine disorders and their impact on overall health.
Consider using diagrams and flowcharts to visualize the interactions between glands, hormones, and physiological processes within the endocrine system.
By mastering these concepts, you will develop a comprehensive understanding of the endocrine system and its vital role in maintaining homeostasis and overall health.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Moving and Controlling the Body
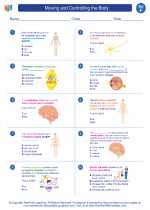
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key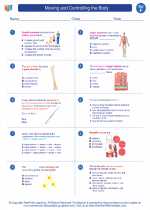
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key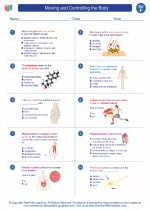
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key