Plant Processes -> infrared radiation
Infrared Radiation
Infrared radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation that falls between visible light and microwave radiation on the electromagnetic spectrum. It has longer wavelengths than visible light, ranging from about 700 nanometers to 1 millimeter.
Properties of Infrared Radiation:
- Wavelength: Infrared radiation has longer wavelengths than visible light, making it invisible to the human eye.
- Heat Transfer: Infrared radiation is often associated with heat transfer. Objects and substances emit and absorb infrared radiation as heat.
- Applications: Infrared radiation is used in various applications, including night vision technology, remote temperature sensing, and infrared spectroscopy.
Sources of Infrared Radiation:
- Sunlight: The sun is a natural source of infrared radiation, with a significant portion of its energy emitted in the infrared range.
- Heat from Objects: All objects with a temperature above absolute zero emit infrared radiation. This is the basis for thermal imaging and heat detection.
- Artificial Sources: Infrared lamps, heaters, and other devices are designed to produce and emit infrared radiation for specific purposes.
Effects of Infrared Radiation:
Infrared radiation has various effects on different materials and living organisms. For example, it can cause heating of surfaces, skin, and tissues, leading to thermal effects. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in the Earth's energy balance and climate regulation.
Study Guide:
To understand infrared radiation better, consider the following study guide:
- Define infrared radiation and explain its position on the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Discuss the properties of infrared radiation, including its wavelength and heat transfer capabilities.
- Explore the sources of infrared radiation and provide examples of natural and artificial sources.
- Examine the applications of infrared radiation in various fields such as technology, medicine, and environmental science.
- Analyze the effects of infrared radiation on materials and living organisms, and discuss its significance in the context of climate and energy balance.
By delving into these topics, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of infrared radiation and its relevance in the world around us.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Plant Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson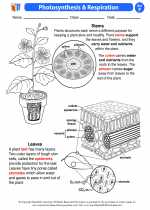
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
