Solids, liquids and gases -> boyle's law
Explanation of Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law can be expressed mathematically as:P1V1 = P2V2
Where: P1 = initial pressure V1 = initial volume P2 = final pressure V2 = final volumeAccording to Boyle's Law, as the volume of a gas decreases, the pressure of the gas increases, and vice versa. This means that if you decrease the volume of a gas, the molecules are forced closer together, which results in more frequent collisions with the walls of the container, leading to an increase in pressure.Study Guide for Boyle's Law
To understand Boyle's Law, it is important to remember the following key points:- Pressure and volume are inversely proportional: As volume decreases, pressure increases, and as volume increases, pressure decreases.
- Temperature and amount of gas must remain constant: Boyle's Law applies only when the temperature and the amount of gas are held constant.
- Mathematical representation: The relationship between pressure and volume can be represented by the equation P1V1 = P2V2.
- Real-life applications: Boyle's Law is relevant in various real-life scenarios, such as scuba diving, where changes in pressure affect the volume of gases in the body.
- Graphical representation: A graph of pressure versus volume for a given amount of gas at constant temperature will show an inverse relationship, forming a curve.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Solids, liquids and gases
Study Guide Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson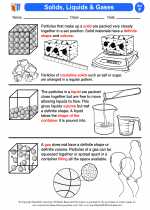 Solids, Liquids & Gases
Solids, Liquids & Gases  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Energy
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Plan an investigation to determine the relationships among the energy transferred, the type of matter, the mass, and the change in the average kinetic energy of the particles as measured by the temperature of the sample.