Inflammation
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection. It is a complex biological process that involves the immune system, blood vessels, and various signaling molecules.
Causes of Inflammation
- Infection: When pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi invade the body, the immune system responds by triggering inflammation to combat the invaders.
- Injury: Tissue damage from physical trauma, burns, or exposure to irritants can lead to inflammation as the body attempts to repair the damage.
- Autoimmune disorders: In conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation.
- Chronic diseases: Conditions like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease can trigger low-grade, long-term inflammation in the body.
Process of Inflammation
The process of inflammation involves a series of events that occur in the affected tissues. It can be divided into several stages:
- Vasodilation: The blood vessels in the affected area widen, allowing more blood to flow to the site of injury or infection. This results in redness and heat in the area.
- Increase in vascular permeability: The blood vessel walls become more permeable, allowing immune cells and fluid containing proteins to move from the bloodstream into the tissues. This causes swelling and pain.
- Immune cell recruitment: White blood cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, are attracted to the site of inflammation to attack and destroy any harmful agents.
- Tissue repair and resolution: Once the threat is neutralized, the inflammation gradually subsides, and the damaged tissues begin to heal.
Study Guide
To study inflammation, you should focus on understanding the causes, process, and effects of inflammation on the body. Here are some key points to consider:
- What are the different causes of inflammation, and how does the body respond to each cause?
- Describe the process of inflammation, including the cellular and molecular events that occur at the site of injury or infection.
- Explain the role of various immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, in the inflammatory response.
- Discuss the differences between acute and chronic inflammation, and give examples of diseases associated with each type.
- Explore the relationship between inflammation and various health conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
By understanding the underlying mechanisms of inflammation, you can appreciate its role in the body's defense and its contribution to various diseases. Additionally, it is important to explore potential treatments and interventions that target inflammation to maintain overall health and well-being.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Solids, liquids and gases

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson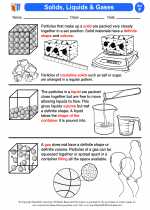
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
