Aquifers: An Overview
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt) from which groundwater can be extracted using a water well. These underground reservoirs hold large amounts of water and are crucial sources of freshwater for human consumption, agriculture, and industrial use.
Formation of Aquifers
Aquifers are formed over long periods of time through the process of infiltration, where precipitation seeps into the ground and accumulates in porous layers of rock or sediment. The water is held within the spaces between particles, such as sand grains or cracks in rocks, creating a storage reservoir for groundwater.
Types of Aquifers
There are different types of aquifers, classified based on their geological characteristics:
- Unconfined Aquifers: These aquifers are not confined by impermeable layers above and are directly influenced by surface water and precipitation.
- Confined Aquifers: Confined aquifers are sandwiched between impermeable layers, which put pressure on the water within the aquifer and can lead to artesian wells.
- Perched Aquifers: Perched aquifers are localized, elevated areas of saturated groundwater separated from the main aquifer by impermeable layers.
Importance of Aquifers
Aquifers are vital for sustaining ecosystems and human activities. They provide a reliable source of water for drinking, agriculture, and industrial processes. Understanding the dynamics of aquifers is essential for sustainable management and conservation of this precious resource.
Study Guide
To understand aquifers, students should focus on the following key points:
- The formation process of aquifers and the role of infiltration in groundwater accumulation.
- The differences between unconfined, confined, and perched aquifers, including their geological characteristics and water accessibility.
- The significance of aquifers in providing freshwater for various purposes and the need for their conservation and sustainable use.
- The methods used to extract groundwater from aquifers, such as wells and pumps, and the potential impacts of over-extraction on aquifer depletion.
- The interconnectedness of surface water and groundwater, and the implications of human activities on aquifer contamination and depletion.
By mastering these concepts, students can gain a comprehensive understanding of aquifers and their significance in the global water cycle and human civilization.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Bacteria and Viruses
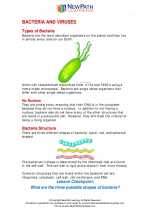
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson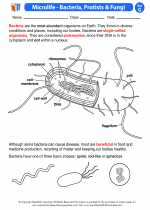
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
