Axon Terminal
The axon terminal, also known as the synaptic knob, is a structure at the end of the axon of a neuron. It is responsible for transmitting signals to the dendrites of other neurons or to target cells such as muscles or glands. The axon terminal contains synaptic vesicles that store neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that relay signals between neurons.
Structure of Axon Terminal
The axon terminal is composed of several key structures:
- Synaptic Vesicles: Small sacs within the axon terminal that store neurotransmitters.
- Neurotransmitters: Chemical messengers that are released from the synaptic vesicles and transmit signals to other neurons or target cells.
- Synaptic Cleft: The small gap between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrite of another, across which neurotransmitters are released.
- Mitochondria: Organelles that provide energy for the axon terminal's activities.
Function of Axon Terminal
The main function of the axon terminal is to transmit signals from one neuron to another or to target cells. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft. These neurotransmitters then bind to receptors on the dendrites of the receiving neuron or on the target cell, leading to the transmission of the signal.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about the axon terminal:
- The axon terminal is located at the end of the axon of a neuron.
- It contains synaptic vesicles that store neurotransmitters.
- Neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal and transmit signals to other neurons or target cells.
- The synaptic cleft is the gap between the axon terminal and the dendrite of another neuron or a target cell.
- Energy for the axon terminal's activities is provided by mitochondria.
Understanding the structure and function of the axon terminal is crucial for comprehending how neurons communicate with each other and how signals are transmitted throughout the nervous system.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Bacteria and Viruses
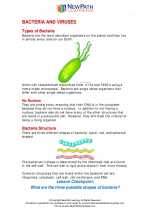
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson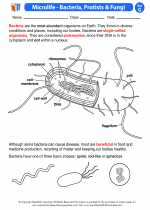
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
