Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a vital structure that encloses the contents of a cell, maintains its integrity, and regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell.
Structure of the Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is primarily composed of a double layer of phospholipid molecules arranged in a bilayer. These phospholipids have a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail. Embedded within this lipid bilayer are proteins, cholesterol molecules, and carbohydrates. The proteins play crucial roles in various cellular functions, including transport, signaling, and cell recognition.
Functions of the Cell Membrane
1. Boundary Formation: The cell membrane acts as a barrier, separating the internal cellular environment from the external surroundings.
2. Transport: It regulates the movement of molecules such as ions, nutrients, and waste products into and out of the cell through various transport proteins and channels.
3. Cell Recognition: The carbohydrates on the outer surface of the membrane are involved in cell recognition and communication.
4. Signal Transduction: Proteins in the membrane play a role in transmitting signals from the external environment to the cell's interior.
Study Guide
To understand the cell membrane thoroughly, it's essential to focus on the following key areas:
- Describe the structure of the cell membrane and the roles of phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates within the membrane.
- Explain the functions of the cell membrane, including boundary formation, transport, cell recognition, and signal transduction.
- Compare and contrast passive transport (diffusion, osmosis) and active transport processes across the cell membrane.
- Explore the concept of membrane fluidity and how it impacts the functioning of the cell membrane.
- Discuss the significance of the cell membrane in maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to environmental changes.
Understanding the cell membrane is crucial in comprehending the fundamental processes that occur within a cell and its interactions with the external environment.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Bacteria and Viruses
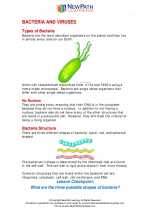
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson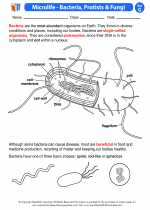
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
