How Electric Motors Work
Electric motors operate based on the interaction between magnetic fields and electric current. When an electric current flows through a wire that is placed in a magnetic field, a force is exerted on the wire, causing it to move. This principle, known as the Lorentz force, forms the basis for the operation of electric motors.
Components of an Electric Motor
Electric motors consist of several essential components, including a stator (stationary part), a rotor (rotating part), a commutator (in some types of motors), and brushes (in some types of motors). The stator contains the stationary coils of wire that produce the magnetic field, while the rotor holds the wire coils that carry the electric current. The commutator, found in DC motors, reverses the direction of the current in the rotor windings, ensuring continuous rotation. Brushes are used to deliver electrical current to the rotor in some motor designs.
Types of Electric Motors
There are various types of electric motors, including DC motors and AC motors. Direct current (DC) motors operate using a constant voltage, while alternating current (AC) motors run on an alternating voltage. Each type has its own set of advantages and applications, making them suitable for different purposes.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are utilized in a wide range of applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery. They are commonly found in fans, pumps, compressors, conveyor systems, and electric vehicles. Understanding the significance of electric motors in modern technology is crucial for appreciating their extensive usage and impact on daily life.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Bacteria and Viruses
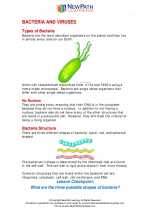
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson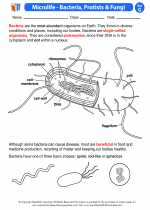
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
