What are macrolides?
Macrolides are a class of antibiotics that are used to treat bacterial infections by inhibiting the growth of bacteria.
How do macrolides work?
Macrolides work by inhibiting the production of proteins in bacteria, which is essential for their growth and survival. By blocking protein production, macrolides effectively stop the growth of bacteria.
What are the common types of macrolides?
The most common macrolide antibiotics include erythromycin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin. These antibiotics are often prescribed to treat respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.
What are the side effects of macrolides?
Common side effects of macrolides include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In some cases, macrolides can also cause allergic reactions and liver problems.
How are macrolides prescribed?
Macrolide antibiotics are typically prescribed by a healthcare professional and should be taken exactly as directed. It's important to finish the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start to feel better before the prescription is finished.
Are there any drug interactions with macrolides?
Yes, macrolides can interact with other medications, so it's important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are currently taking before starting a macrolide antibiotic.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Bacteria and Viruses
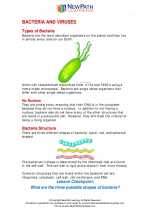
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson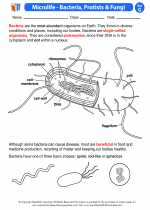
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
