Symbiosis
Symbiosis is a biological interaction between two different species. These interactions can be categorized into three main types: mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
Mutualism
Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit from the interaction. An example of mutualism is the relationship between bees and flowers. Bees obtain nectar from the flowers, while the flowers are pollinated by the bees.
Commensalism
Commensalism is a symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed. An example of commensalism is the relationship between barnacles and whales. Barnacles attach themselves to the skin of whales, obtaining a place to live and feed, while the whales are unaffected by this interaction.
Parasitism
Parasitism is a symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits at the expense of the other. An example of parasitism is the relationship between ticks and mammals. Ticks feed on the blood of mammals, which can harm or even kill the host.
Study Guide
- Define symbiosis and give examples of each type of symbiotic relationship.
- Explain the benefits and drawbacks of each type of symbiotic relationship.
- Compare and contrast mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
- Discuss the ecological importance of symbiotic relationships in maintaining ecosystem balance.
- Research and present a case study of a specific symbiotic relationship in nature.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Bacteria and Viruses
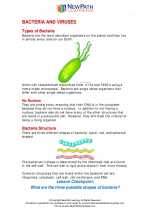
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson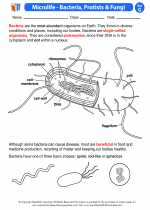
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
