What is Altruism?
Altruism refers to selfless behaviors or actions that are performed to benefit others, often without any expectation of personal gain or reward. It is a fundamental aspect of human social behavior and has been the subject of extensive study in the fields of psychology, sociology, and evolutionary biology.
Examples of Altruistic Behaviors
Altruistic behaviors can take various forms, such as helping a stranger in need, donating to charity, volunteering time and resources for a cause, or even risking one's own safety to protect others. These actions are driven by empathy, compassion, and a sense of moral obligation to contribute to the well-being of others.
Theories of Altruism
Several theories have been proposed to explain the origins and motivations behind altruistic behavior, including:
- Biological altruism: This theory suggests that altruistic behaviors may have evolved as a result of natural selection, where individuals may sacrifice their own well-being to ensure the survival and reproductive success of their kin or group.
- Reciprocal altruism: According to this theory, individuals may engage in altruistic acts with the expectation that the favor will be reciprocated in the future, leading to mutual benefit.
- Empathy-altruism hypothesis: This hypothesis proposes that empathetic concern for others can lead to altruistic behavior, as individuals are motivated to reduce the suffering of others due to their emotional connection.
Factors Influencing Altruism
Altruistic behavior can be influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Personal values and beliefs: Individuals with strong moral and ethical principles may be more inclined to engage in altruistic acts.
- Social norms and culture: Cultural practices and societal expectations can shape altruistic behaviors within a community or group.
- Empathy and emotional empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of others can drive altruistic actions, especially in response to witnessing someone in distress.
- Costs and benefits: The perceived costs, risks, and potential benefits associated with altruistic acts can influence an individual's decision to engage in such behaviors.
Applications of Altruism
Understanding altruism has practical implications in various domains, including:
- Social and community development: Altruistic behaviors contribute to the creation of supportive and cohesive communities, fostering a sense of cooperation and mutual aid.
- Humanitarian efforts: Altruism plays a crucial role in humanitarian aid, disaster relief, and philanthropic initiatives aimed at addressing the needs of vulnerable populations.
- Conflict resolution and peacebuilding: Promoting altruistic attitudes can help in mitigating conflicts, promoting reconciliation, and building sustainable peace in societies.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson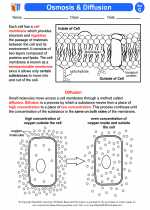
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key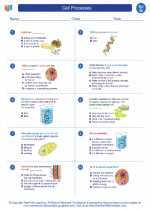
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key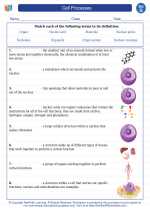
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
