Biodiversity
Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, refers to the variety and variability of life on Earth. It encompasses the diversity of species, genetic diversity within each species, and the variety of ecosystems in which they live. Biodiversity is crucial for the healthy functioning of ecosystems and provides a wide range of benefits to humans, including food, medicine, and ecosystem services such as air and water purification, pollination, and climate regulation.
Types of Biodiversity
There are three main types of biodiversity:
- Species Diversity: This refers to the variety of different species within a specific area. It includes both the number of species present and their relative abundance.
- Genetic Diversity: This refers to the variation of genes within a species. It is important for the adaptation and survival of species in changing environments.
- Ecosystem Diversity: This refers to the variety of different ecosystems within a region. Ecosystem diversity includes different habitats, communities, and ecological processes.
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is essential for the following reasons:
- Ecological Stability: Biodiverse ecosystems are more resilient and can better withstand environmental changes and disturbances.
- Human Well-being: Biodiversity provides essential resources such as food, medicine, and clean water, and contributes to cultural and recreational value.
- Economic Value: Biodiversity supports industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and ecotourism, contributing to local and global economies.
- Ecosystem Services: Biodiverse ecosystems provide services like air and water purification, pollination, and climate regulation, which are vital for human survival.
Threats to Biodiversity
Human activities, such as habitat destruction, pollution, overexploitation of natural resources, and climate change, pose significant threats to biodiversity. These activities result in species extinction, loss of genetic diversity, and degradation of ecosystems. Conservation efforts are essential to mitigate these threats and preserve biodiversity for future generations.
Study Guide
To study and understand biodiversity, consider the following key points:
- Define biodiversity and explain its significance.
- Identify and describe the three main types of biodiversity.
- Discuss the importance of biodiversity for ecological stability, human well-being, and ecosystem services.
- Explore the threats to biodiversity and their implications for the environment and human societies.
- Research and discuss specific examples of conservation efforts and their impact on biodiversity preservation.
Understanding biodiversity is crucial for appreciating the interconnectedness of life on Earth and the importance of preserving and protecting the natural world.
[Biodiversity] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson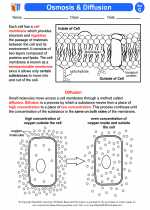
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
