Current Electricity
Current electricity is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is the movement of electrons through a closed path or circuit. The flow of electrons is measured in amperes (A), and the rate at which the charge flows is called electric current.
Electric Circuit
An electric circuit is a closed loop through which an electric current flows. It consists of a source of electrical energy (such as a battery), conductors (wires) to carry the current, and electrical components (such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors) to perform work.
Electric Current
Electric current is the flow of electric charge. It is represented by the symbol 'I' and is measured in amperes (A). The direction of the current is from the positive terminal of the battery to the negative terminal, although the actual flow of electrons is from negative to positive.
Types of Current
There are two main types of electric current: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). DC flows in one direction, while AC alternates in direction periodically. DC is commonly used in batteries and electronic devices, while AC is used in homes and businesses to power electrical appliances.
Ohm's Law
Ohm's law describes the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit. It states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Study Guide:
- Define electric current and explain its measurement.
- Describe the components of an electric circuit.
- Differentiate between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC).
- State Ohm's law and explain its significance in electrical circuits.
- Discuss the applications of current electricity in everyday life.
- Perform calculations involving current, voltage, and resistance using Ohm's law.
- Identify and explain the function of various electrical components in a circuit (e.g., resistors, capacitors).
[Current Electricity] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson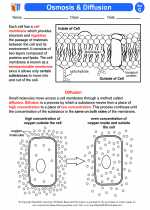
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
