Eskers: Formation and Characteristics
An esker is a long, winding ridge of stratified sand and gravel, typically formed by the deposition of glacial meltwater. These features are found in areas that were once covered by glaciers during the last ice age. Eskers are often several kilometers long and can reach heights of up to 30 meters.
Formation of Eskers
Eskers are formed as a result of the deposition of sediments by meltwater streams flowing within or beneath glaciers. As the glaciers melt, the sediments are deposited in the form of a sinuous ridge. Over time, the ice completely melts, leaving behind the ridge-shaped landform known as an esker.
Characteristics of Eskers
- Shape: Eskers typically have a long, winding shape, resembling a snake or a river meander.
- Composition: They are composed of stratified sand and gravel, which were originally deposited by glacial meltwater.
- Location: Eskers are often found in regions that were covered by glaciers, such as northern Europe, Canada, and parts of the United States.
- Use: Eskers are often sources of high-quality sand and gravel, and they are sometimes used as locations for transportation routes, such as roads and railways.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about eskers:
- Describe the formation process of eskers, including the role of glacial meltwater in their creation.
- Explain the characteristics of eskers, including their shape, composition, and typical locations.
- Discuss the potential uses of eskers and their significance in geological and human contexts.
- Identify regions of the world where eskers are commonly found and explain the environmental conditions that favor their formation.
Be sure to study the formation, characteristics, and significance of eskers in preparation for your test or exam!
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson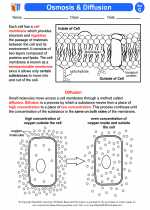
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
