Instinctive Behavior
Instinctive behavior is a type of innate, unlearned behavior that is genetically programmed in an organism. These behaviors are typically present at birth and are essential for the survival and reproduction of the organism. Instinctive behaviors can be seen in a wide range of organisms, from insects and birds to mammals, including humans.
Types of Instinctive Behaviors
There are several types of instinctive behaviors observed in animals:
- Migration: The seasonal movement of animals from one region to another, often for the purpose of finding food, mating, or nesting.
- Homing: The ability of an animal to find its way back to its home or a specific location, often over long distances.
- Hunting and Foraging: The behaviors related to locating, capturing, and consuming food.
- Parental Care: Behaviors related to caring for and protecting offspring, such as nesting, feeding, and grooming.
- Territoriality: Establishing and defending a territory for feeding, mating, or raising young.
- Defense Mechanisms: Instinctive responses to threats or danger, such as fleeing, hiding, or fighting.
Examples of Instinctive Behaviors
Some examples of instinctive behaviors in animals include:
- Salmon Migration: Salmon returning from the ocean to their freshwater spawning grounds to reproduce.
- Bird Migration: Birds flying thousands of miles to find suitable breeding and feeding grounds.
- Spider Web Building: Spiders constructing intricate webs to capture prey.
- Imprinting in Ducks: Ducklings following and imprinting on the first moving object they see, often their mother.
- Honeybee Dance: Honeybees performing a “waggle dance” to communicate the location of food sources to other members of the hive.
Importance of Instinctive Behaviors
Instinctive behaviors are crucial for the survival and reproductive success of organisms. They allow animals to adapt to their environments, find resources, avoid predators, and reproduce effectively. These behaviors are shaped by natural selection and have evolved over time to increase the chances of an organism’s survival and the passing on of its genes to the next generation.
Study Guide
To better understand instinctive behavior, consider the following study guide:
- Define instinctive behavior and provide examples of instinctive behaviors in different animal species.
- Explain the role of instinctive behaviors in the survival and reproduction of organisms.
- Compare and contrast instinctive behaviors with learned behaviors, providing examples of each.
- Discuss the evolutionary significance of instinctive behaviors and how they contribute to the fitness of an organism.
- Research a specific animal species and analyze its instinctive behaviors in relation to its ecological niche and survival strategies.
By exploring these topics and examples, you can gain a deeper understanding of instinctive behavior and its importance in the animal kingdom.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson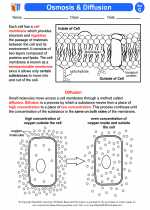
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
