Nerves
Nerves are part of the body's nervous system, which is responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body and the brain. The nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes the nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
Structure of Nerves
Nerves are made up of nerve cells, or neurons. Neurons have a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles, while the dendrites receive signals from other neurons. The axon is a long, thin fiber that transmits signals to other neurons or to muscles or glands.
Function of Nerves
Nerves transmit electrical signals, called nerve impulses, throughout the body. These impulses allow the body to sense and respond to its environment, control movement, and regulate bodily functions such as heart rate and digestion.
Types of Nerves
There are three main types of nerves: sensory nerves, motor nerves, and mixed nerves. Sensory nerves carry signals from the body's sensory organs (such as the eyes, ears, and skin) to the CNS. Motor nerves carry signals from the CNS to the body's muscles and glands, controlling movement and bodily functions. Mixed nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers, allowing for two-way communication between the CNS and the rest of the body.
Study Guide
- What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
- Describe the structure of a neuron.
- What is the function of nerves in the body?
- Identify the three main types of nerves and their functions.
- How do nerves transmit signals throughout the body?
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson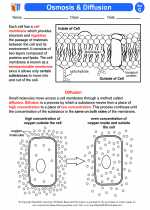
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
