Catalysis: Explanation and Study Guide
What is Catalysis?
Catalysis is the process in which a substance known as a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. The catalyst itself remains unchanged at the end of the reaction.
Types of Catalysts:
- Heterogeneous Catalysts: These catalysts are present in a different phase from the reactants. For example, a solid catalyst in a liquid or gaseous reaction.
- Homogeneous Catalysts: These catalysts are present in the same phase as the reactants, such as a dissolved catalyst in a liquid reaction.
- Biological Catalysts: Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate biochemical reactions in living organisms.
How Does Catalysis Work?
A catalyst works by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. This allows the reactant molecules to more easily reach the transition state and form the products. The catalyst achieves this by forming temporary bonds with the reactant molecules, stabilizing the transition state, and facilitating the breaking and formation of chemical bonds.
Applications of Catalysis:
- Catalysis is widely used in industrial processes such as the production of fuels, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
- It is essential in environmental protection, for example, in catalytic converters that reduce emissions from vehicles.
- Biological catalysis, through enzymes, is crucial for the functioning of living organisms and is utilized in various biotechnological processes.
Study Guide:
To understand catalysis, it is important to grasp the following concepts:
- The role of a catalyst in lowering the activation energy of a reaction.
- The difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts, and their respective examples.
- The mechanism of catalysis, including the formation of temporary bonds and stabilization of transition states.
- Real-world applications of catalysis in industrial and environmental contexts.
- The significance of biological catalysts, such as enzymes, in biochemical reactions.
Studying catalysis involves exploring the principles of chemical kinetics, reaction mechanisms, and the properties of different types of catalysts. Additionally, conducting experiments and analyzing catalytic reactions can provide practical insights into the subject.
By comprehensively understanding catalysis, students can appreciate its importance in various fields and its impact on the efficiency and sustainability of chemical processes.
Happy studying!
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Earthquakes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson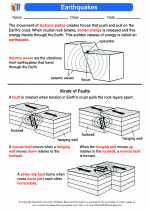
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
